The Regulation of the EU parliament 2016/679 on the protection of personal data GDPR will take effect on May 25, 2018. We have studied its main principles, new requirements, and possible fines for their violation. In this article, we will share some points an email marketer should take into account to work in compliance with the new legislation.
What is the GDPR
Digital marketing is based on the analysis of large volumes of consumer data. This information allows companies to create relevant products or services and achieve high results.
Websites save cookie files on their users’ PCs to find out about their preferences; mobile phone operators track incoming and outgoing calls and record them. Facebook employs face recognition to identify and tag users in photos. Instagram arranges posts in your feed depending on the number of views, likes, and comments. However, data should be processed fairly and lawfully. That is why the new rules of data protection — the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) — are coming in force. According to this Regulation, companies that collect, store, use customers’ personal data or process it for other companies, should revise three main aspects of data processing:
- Data collection.
- Processing, storage, adaptation, discarding or transferring of the collected information.
- Protection of personal data.
Who does the GDPR apply to?
In addition to the data received and processed by the companies located in the EU, the GDPR will apply to any personal information transferred outside the EU zone. In other words, if a US company collects data from the EU citizens, it will be subject to the same data protection requirements as any company based in France, Germany, or any other country of the European Union.
Responsible Parties
Let’s see who is involved in the collection, processing, and storage of personal data and what functions they perform:
- Data subject is an individual who provides their personal data.
- Data controller is an individual or a legal person that receives the personal data and determines the purposes and means of its processing. The term refers to any business that collects and makes use of customers’ personal data. It informs the users about the purposes of data collection, documents its processing, evaluates the attendant risks, safeguards sensitive information, and notifies the supervisory authorities and the users about any problems that may arise in the process.
- Data processor is the contractor who collects, processes and stores personal data on behalf of the Data controller. In email marketing, this role is commonly played by email services. In case of any infringement, the processor informs the controller about it.
- Supervisory authority is an official body that supervises personal data processing. It determines the severity of data security violation and imposes appropriate fines on the responsible parties.
Penalties for non-compliance
Potential fines for non-compliance with the GDPR are severe. They are divided into two groups depending on the type of infringement.
Up to €10 Million
A company can be fined up to the greater of €10 Million or 2% of its annual turnover in the previous year for breaching the data controller’s and the processor’s liabilities. These include consent for processing a child’s personal data and privacy protection.
Up to €20 Million
A fine that amounts to the greater of €20 Million or 4% of the company’s annual turnover will be imposed for violation of the basic GDPR rules, such as those that regulate the rights of data subjects, principles of data processing and transferring, or consent requirements.
If the breach is not serious, the company will get a reprimand.
Now let’s take a closer look at the key principles of data processing in accordance with the GDPR.
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
The company should explain clearly and explicitly why and on what conditions it collects personal data. The users should get free access to this information, which will make them aware of the ways the collected data will be used and conscious of the risks they face, rules they have to comply with, and the rights they can exercise with regard to their personal information.
Email marketers often use lead-magnets to attract subscribers. They offer incentives, such as free trial periods, articles, manuals, or other useful content, in exchange for the user’s contact details.
For this method of data collection to comply with the GDPR requirements, make sure you receive explicit consent of the users for storage and processing of their personal information. Such consent can be evidenced by a clear affirmative action of the subscriber, such as
- ticking a checkbox,
- choosing specific account settings,
- any other action or document that proves the subscriber’s awareness of the data processing methods.
How to get explicit consent in email marketing
Encourage users to review the privacy policy and the terms of use before they subscribe. In these documents, explain in detail how you collect, systematize, store, adapt and delete customer data.
We recommend using double opt-in subscription setting to build your mailing list. Unlike single opt-in, where the end user only inserts their email address and presses the subscription button, the double opt-in subscription requires the user to also click on the link or press a button in the confirmation email. This way the subscriber demonstrates genuine consent for processing and storage of their personal information.
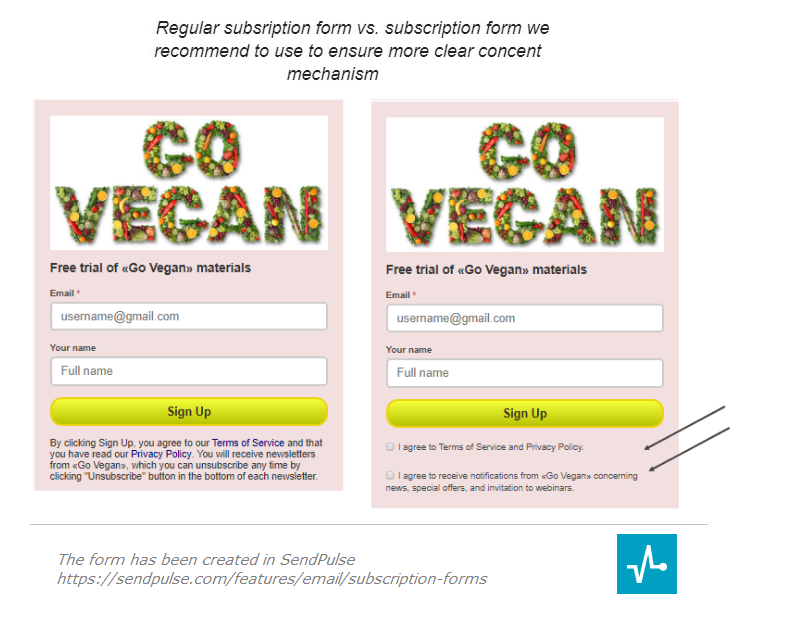
As an alternative, to safeguard yourself from unwanted accusations, it’s better to add two separate opt-in checkboxes to your subscription form as you can see in the example below. The user will confirm having reviewed the privacy policy and the terms of use in the first checkbox and express their consent to receive email from your website in the second one. However, make sure you do not tick the checkboxes beforehand — such “forced” consent violates the GDPR principles.
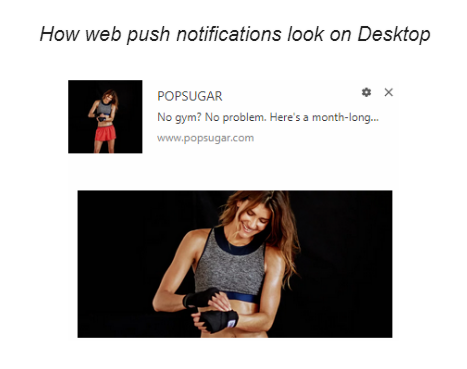
Feel free to make use of other communication channels. There are several other ways to contact your potential clients without emailing them. Web push notification is another great way to engage new visitors. When subscribing to web push messages, users do not need to provide any personal data, yet they express their explicit consent by pressing the “Allow Notifications” button.
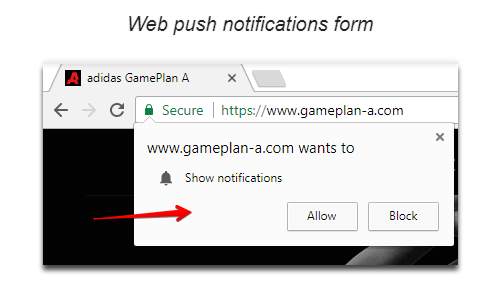
With a web push, you can notify the user about news, special offers, and other important events.
Data minimization
The Regulation encourages marketers to collect only relevant customer data that will be used for specific purposes. If you need to know the subscriber’s clothing size or the color they prefer, make sure you explain why this information is important. Otherwise, it is better to refrain from collecting such data.
Avoid requesting extra information
We recommend limiting the collected information and carefully reviewing the questions posed in subscription forms and questionnaires.
For example, a tourist company Massachusetts Office of Travel & Tourism adds a survey to its Halloween email campaign, limiting its questions to those that can help the company offer relevant tours to its customers.
By pressing the “Take survey” button, the subscriber goes to the pages that require them to provide the following information:
- age,
- information about children,
- cities in Massachusetts they would like to visit,
- preferred time for travelling: weekends or work days,
- attitude to Halloween-themed entertainment.
Accuracy
According to this principle, the user can have their personal information changed if it turns out to be irrelevant or outdated. Such requests should be processed timely, so you may need to develop an effective data updating system.
Encourage your subscribers to update their preferences
Add a link to the settings page to your email (email preferences, update preferences, manage preferences) or use a service that will allow for updating customer data. If the user’s account has a settings page, they can click on the link and update their personal information themselves. Take a look at the way Astley Clarke handles this task in its email.
Here is what the user can change in their Astley Clarke profile.
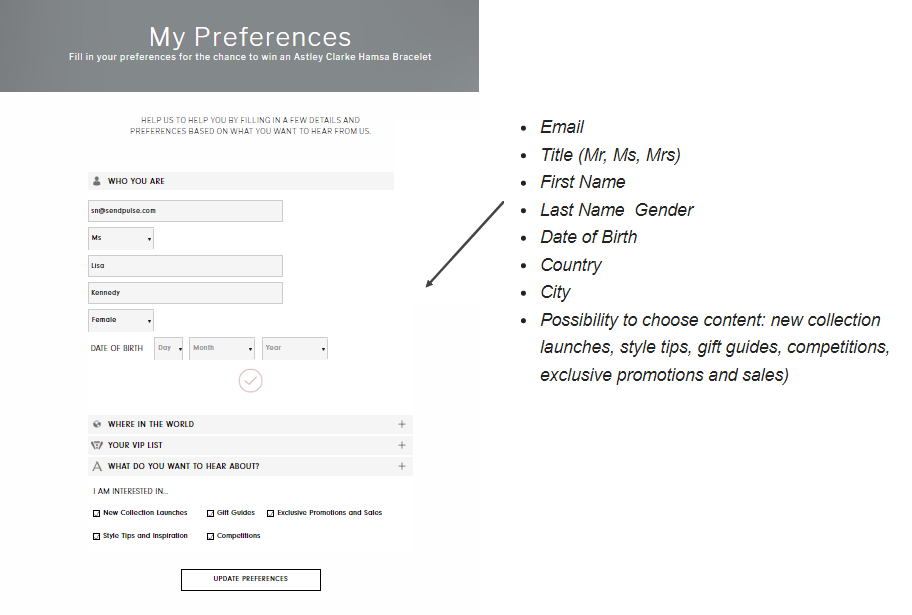
Purpose limitation
Collect and use personal data only for the specified purposes. Do not conceal your intentions from the users and always ask them to confirm their consent if you need to use their data for a different purpose.
Make sure your subscribers know the truth
Not to seek the users’ consent too often, think of possible purposes of data collection beforehand and clearly indicate them in your privacy policy.
For example, personal data can be necessary for
- account registration,
- helpdesk queries,
- service or product provision,
- sending news, special offers, or updates about the product.
Storage limitation
Companies are allowed to store customer data only as long as it is necessary for its processing.
Consider the data storage policy
In a separate section of the privacy policy, describe how long the data will be stored and what will happen to it if the subscriber decides to opt out.
Integrity and confidentiality
The company is responsible for the security of the collected data, which means that it should protect it from unlawful processing and against accidental loss, damage, or destruction.
In case of data breach, make sure you notify the user and the national Data Protection Authorities within 72 hours after the accident. The notification must include the report on the investigation of the incident, possible causes, and the description of any interventions that have been undertaken. All these are necessary for a timely reaction on the part of the data subjects and minimization of financial losses and other unwanted consequences.
Ensure that the data is protected and encourage the users to do that
It is illegal to buy, transfer, or disclose personal information. Advise the registered users to make their password reliable, change it from time to time, and never to disclose it to any third party.
Transfer the personal data from Excel spreadsheets and Google Docs files to your CRM system to enhance the security and convenience of data processing.
Data Subject Rights
New GDPR requirements extend the rules of the EU citizens in regards to control of their personal data. The data controller is responsible for granting these rights to the users.
Data access
Do not limit the users’ access to data. Inform them about who uses the collected data and for what purposes. Indicate the data storage period.
Data portability
Now the customer is eligible for receiving a digital copy of their personal data within 30 days upon request. This development makes it easier for the user to switch to a different service.
Data erasure
The user may revoke their consent for data processing and send a request for its erasure. Make sure you react to such requests without any delays. For email marketing, it means to delete the customer data from all mailing lists. A direct unsubscribe link sent with an email will speed up the process. In other words, if the subscriber does not want to receive emails from your website, they can simply click the corresponding button or “Unsubscribe” link.
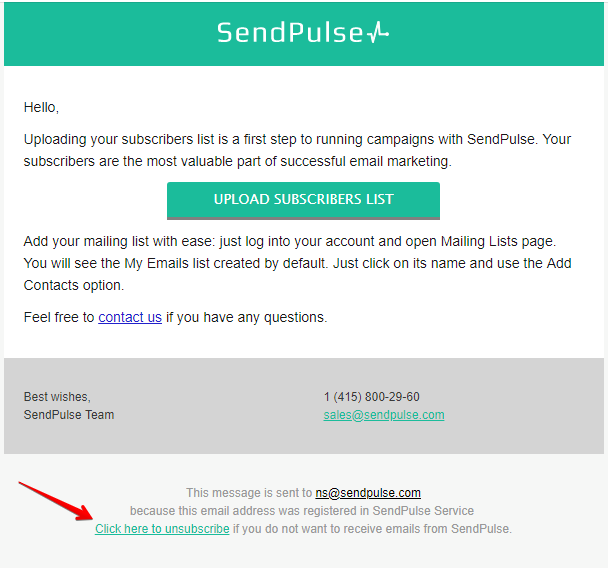
In SendPulse service, you will not have to delete the data of each unsubscribed user manually. Email addresses of such users are transferred to the unsubscribed recipients list and the email is not delivered to those addresses.
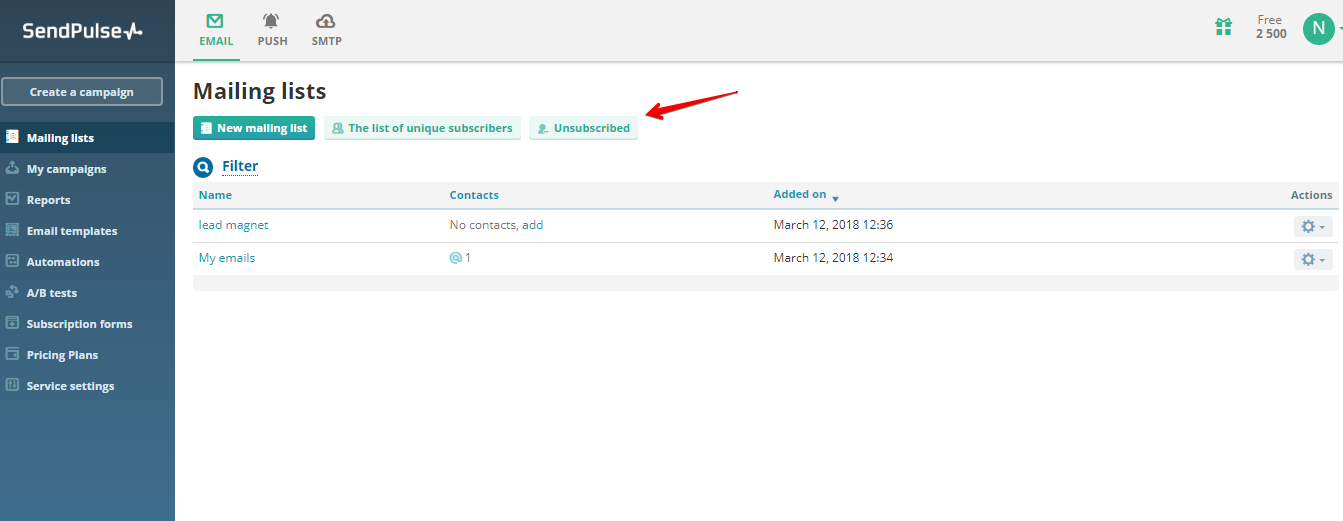
Data processing preferences
If the user does not like the idea of automated data processing, they may request for their profile to be filled in manually. Describe in your privacy policy how you handle manual data processing and who carries it out.
Child protection
To collect personal data of children under the age of 16, make sure you get the parental consent. Do not forget to indicate in the privacy policy how exactly the children will subscribe to the email.
Summing up
To comply with all the GDPR requirements and avoid potential fines, we advise to start with these seven steps:
- Choose the opt-in setting to build your mailing list.
- Add two checkboxes to your subscription form, namely, “I have reviewed the privacy policy and the terms of use” and “I agree to receive notifications from the service.”
- Do not collect any other information apart from what you require for your specific purposes and inform your users about them.
- Include a link to the “manage preferences” page for the subscriber to change the outdated information themselves.
- Develop mechanisms to safeguard personal data from disclosure, damage, or loss.
- Review your current mailing list.
- The email addresses of the subscribers who have not expressed explicit consent for collection and processing of their personal data should be resubscribed or deleted. Request them to confirm their consent for receiving your email and inform them about the new rules of data collection that are reflected in your company’s privacy policy.
Disclaimer: This article can hardly serve as legal advice for your company to follow in compliance with the GDPR. We have provided this information to help you better understand how we have addressed some important legal points. It is not the same as legal advice, where an attorney applies the law to your specific circumstances, so, we recommend that you consult an attorney to get advice on your interpretation of this information or its accuracy.